For protecting your beautiful skin from harmful UV sun rays, its crucial to incorporate sunscreen in your daily Skincare routine. This article will help you to explore the importance of sunscreen, its type, how to use it efficiently and additional tips for sun protection.
Why Sunscreen Routine is Important ?
- Protection against UV Rays- Sun rays are of two types; UVA and UVB. UVA rays deeply penetrate into the skin leading to aging and skin damage. UVB rays causes sunburn and direct DNA damage leading to skin cancer.
- Anti-aging –Sun exposure causes skin aging leading to fine lines, dark spot, wrinkles. Sunscreen protects against photoaging and maintain youthful skin appearance.
- Hyperpigmentation– Sunscreen helps to reduce and prevent dark spot and gives even tone skin.
- Skin Cancer- Risk of skin cancer can be reduced by regular use of sunscreen routine.
Table of Contents
Types of Sunscreen:
On the basis of active ingredient and mechanism of action Sunscreens are classified into two types; Physical (Mineral) and Chemical sunscreen.
1. Physical or Mineral Sunscreens–
- Mechanism: They turn into small shield of skin after application. They sit on the skin’s surface and deflect and scatters UV rays, stopping them to reach the skin.
- *Key Ingredients*:
- 1. Zinc Oxide: it provides protection against various types of rays, especially broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays.
- 2.Titanium Dioxide: it is effective only against UVB and short-wave UVA rays.
- Positive Aspects:
- Physical Sunscreens are effective as soon as applied
- They are suitable to sensitive skin and does not cause irritation.
- They are more stable and last longer in direct sunlight.
- Negative Aspects:
- Physical sunscreens leave a white cast on the skin. On darker skin tones it looks awkward sometime.
- It is available in only thick consistency, so it feels heavier and less comfortable.
2.Chemical Sunscreens–
- Mechanism- Chemical sunscreens get absorb into the skin, then absorb UV rays and convert it into heat, then released heat from body.
- Key Ingredients:
- 1. Avobenzone: Offers broad-spectrum UVA protection.
- 2. Octocrylene: Provide UVB protection and stabilizes other sunscreen ingredients.
- 3. Oxybenzone: provide broad-spectrum protection but is a common allergen and can be environmentally harmful.
- 4. Homosalate, Octinoxate, Octisalate: Provide UVB protection.
- Positive Aspects:
- They are Cosmetically elegant because they can be formulated as a lightweight creams or gel and don’t leave white cast.
- They are super lightweight, easily spreads on skin surface and absorbs quickly.
- Negative Aspects:
- If you ae doing swimming or nothing you have to reapply it more frequently.
- Irritation or allergic reaction cause by some chemical filters
- Some chemical ingredients can harm marine life.
Broad-Spectrum Protection
Broad spectrum protection which means protection against UVA and UVB rays is a crucial feature of any sunscreen. This ensures the prevention against sun burn, premature aging and skin cancer.
SPF (Sun Protection Factor)
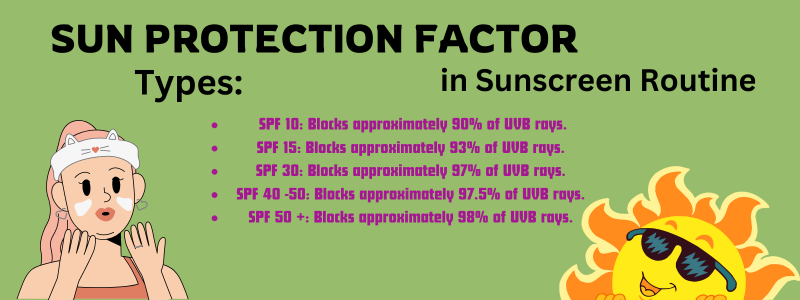
SPF measures a sunscreen’s ability to protect against UVB rays, which cause sunburn leading to suntan and hyperpigmentation.
Types:
- SPF 10: Blocks approximately 90% of UVB rays.
- SPF 15: Blocks approximately 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: Blocks approximately 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 40 -50: Blocks approximately 97.5% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50 +: Blocks approximately 98% of UVB rays.
Choosing the Right SPF:
- If you spent more time indoor then minimum SPF 30 is sufficient for everyday use.
- For prolonged outdoor activities or tropical environment, use minimum SPF 50 or 50+ Sunscreens for better protection.
Application Tips for Sunscreen
- Amount: approx. 01 tablespoon of sunscreen is recommended to cover all sun exposed body part.
- Timing: apply sunscreen 30mins before sun exposure to allow it to sit properly on skin surface.
- Layering: sunscreen application should be a last step in your morning skincare routine
- Reapplication: reapplication is necessary after every two or three hours.
- Coverage: Don’t forget to apply sunscreen on ears, neck and top of the feet.
- Do not apply sunscreen at night time
Sunscreen Routine with Makeup and Skincare Products
- Many makeups and skincare product other than sunscreens now include Sun Protection Factor.
- SPF used in these products do not offer adequate protection, so do not replace sunscreen with such products with little spf.
- Always use a dedicated sunscreen for sun protection.
Sunscreen Myths and Facts
- Myth- one application of sunscreen lasts all day.
- Fact- Sunscreen needs to reapply after every two or three hours.
- Myth- You Don’t need sunscreen routine on cloudy days
- Fact- up to 80-85% UV rays can penetrate the clouds, so sunscreen is much needed.
- Myth- Darker skin tones don’t need sunscreen.
- Fact- Darker skin produces more melanin, which naturally offers some protection against sun, but people with darker skin still need to apply sunscreen to prevent sun burn and skin cancer.
- Myth- it prevents body to absorb Vitamin D.
- Fact- Sunscreen routine does not significantly impact vitamin D, but you can manage it through diet and supplements.
- Myth- To protect the face, makeup is enough.
- Fact- Makeup provide only additional layer to skin, does not protect against UV rays.
- Myth- Sunscreen is waterproof
- Fact- It can be sweat proof or water proof ; but after swimming or sweating you have to apply sunscreen.
Environmental and Health Considerations
- Use sunscreens free from following chemicals which can harm marine life and our health.
- Oxybenzone
- Avobenzone
- Homosalate
- Octinoxate
- Octocrylene
- Cinoxate
- Dioxybenzone
- Ensulizole
- Meradimate
- Padimate O
- Sulisobenzone
- Octisalate
- Aminobenzoic acid
- Trolamine salicylate
- Always patch test the new sunscreen.
- Do not apply sunscreen to 6-month-old babies. Use Sunscreens specifically formulated for children.
- Sunscreen routine for pregnant women- Chemical sunscreens are not safe for pregnant lady or lactating mother. They can use physical sunscreen.
Sunscreen and Lifestyle
- Use tinted sunscreen for protection with cosmetic finish.
- Use spray or sticks for easy application.
- Use water resistance sunscreen for activities involving water or sweating.
- Even if You are spending your whole day indoor, incorporate sunscreen into your daily routine.
- For comprehensive protection always complement sunscreen with any protective cloth like hat or scarf and broad sunglasses.
- Use sunscreens with infused antioxidants like vitamin C, Hyaluronic acid, kojic acid to get extra benefit for skin health.
Conclusion:
- Sunscreen routine is inseparable part of morning skincare routine, offering protection against harmful UVA and UVB rays.
- Regular sunscreen application prevents the skin cancer risk, and premature aging.
- To maintain optimal skin health, understanding of different type, application techniques and key ingredient is necessary.
- Always choose broad spectrum sunscreen with minimum SPF 30 for better protection.


2 thoughts on “Shield Your skin: A comprehensive guide to Sunscreen Routine”
Comments are closed.